
- #CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB FOR FREE#
- #CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB HOW TO#
- #CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB INSTALL#
- #CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB SOFTWARE#
- #CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB PASSWORD#
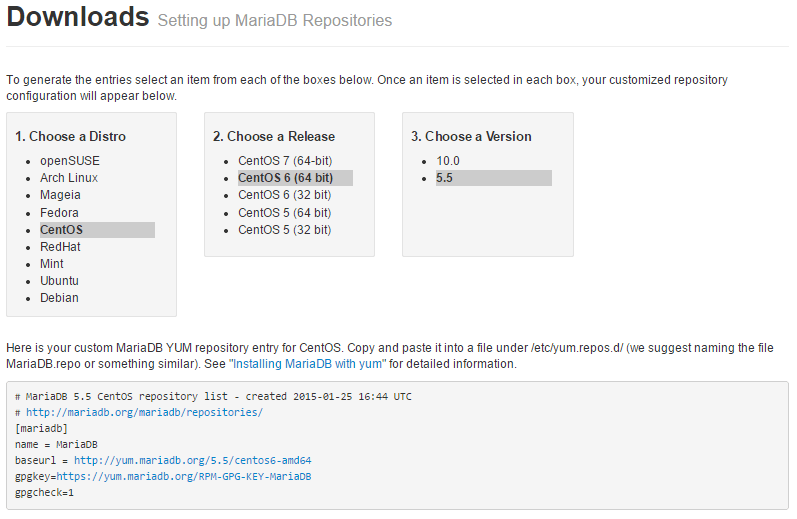
Or you can change the version number in the following commands. , Then right-click and copy the location of the link. If you don’t want to create an account, you can locate the text “No thanks, just start my download. Instead, they lead to a next page where you are prompted to sign in or create an account. Note that the download links do not lead directly to the files.
#CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB INSTALL#
To install MySQL, we need to visit Yum repository of MySQL community, which provides packages for MySQL.

To install MySQL on CentOS 7, follow these steps: MariaDB is fully compatible with MySQL and can be replaced almost transparently. When CentOS 7 released, MySQL was removed from the standard repositories in favor of MariaDB.
#CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB SOFTWARE#
It is part of the LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP), a collection of software used for servers.
#CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB FOR FREE#
MySQL is a popular DBMS for free and open-source database management.
#CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB HOW TO#
We hope this tutorial was enough Helpful.In this tutorial, we are going to see how to install MySQL on CentOS 7. – You will see the Grafana Dashboard as shown below:
#CENTOS 7 INSTALL MYSQL INSTEAD OF MARIADB PASSWORD#
– After Grafana is successfully installed, open the web browser and type the grafana server IP address (with port 3000) Log in to the Grafana Dashboard using default user “ admin” and password “ admin“. ~]# firewall-cmd -permanent -add-port= 3000/tcp If you are using a firewall, open the port using the firewall-cmd command as shown below. – By default, Grafana is running on port 3000. – After the installation, we need to Enable and start the Grafana at Boot System using the following command: ~]# systemctl enable grafana-serverĬreated symlink from /etc/systemd/system//rvice to /usr/lib/systemd/system/rvice. # If you use session in https only, default is false # postgres: user=a password=b host=localhost port=5432 dbname=c sslmode=disable # mysql: go-sql-driver/mysql dsn config string, e.g. # file: session dir path, is relative to grafana data_path # Either "memory", "file", "redis", "mysql", "postgres", default is "file"
# If the password contains # or you have to wrap it with trippel quotes. Type = mysql host = 127.0.0.1:3306 name = grafana user = grafana # Either "mysql", "postgres" or "sqlite3", it's your choice # as seperate properties or as on string using the url propertie. # You can configure the database connection by specifying type, host, name, user and password – Edit the grafana.ini configuration file as below: ~]# vi /etc/grafana/grafana.ini – Backup the grafana.ini configuration file before starting using the following command: ~]# cp /etc/grafana/grafana.ini In this tutorial, we will install using rpm package installation. – Grafana provides two ways for installation, using the rpm package and using the yum repository. MariaDB > grant all privileges on grafana.* to identified by " Password" Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. Server version: 5.5.56-MariaDB MariaDB ServerĬopyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.

– Connect to the MariaDB/MySQL and create a Grafana Databse and ~]# mysql -u root -p – Don’t forget to set a password for the root using mysql_secure_installtion, take a look to this tutorial: Securing MySQL server / Mariadb with mysql_secure_installation – Use the following commands to enable and start MariaDB/MySQL at system boot ~]# systemctl enable mariadbĬreated symlink from /etc/systemd/system//rvice to /usr/lib/systemd/system/rvice. Step 1./ Install MariaDB/MySQL and Create Grafana Databaseįirst of all, we need to install MariaDB/MySQL ~]# yum install mariadb-server In this tutorial, we will show you how to install and setup Grafana using MySQL/ MariaDB database on CentOS 7 or RHEL 7. By default it is configured to use sqlite3 which is an embedded database. Grafana needs a database to store users, dashboards and session (and other things). Grafana allows you to query, visualize, alert on and understand your metrics with the ability to manage and create your own dashboard for your apps or infrastructure performance monitoring.
It offers support for Graphite, Elasticsearch, Prometheus, Zabbix and many more databases. Grafana is an open source data visualization and monitoring suite.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
